08/12/2022 – China — auf Deutsch lesen
Slowing global cotton consumption
The decline in China yarn imports led to lower cotton consumption in major yarn exporting countries such as India, Vietnam, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan.
China is by far the largest cotton yarn importer and thus a major driver of global cotton lint consumption. China’s spinning mills do not produce enough yarn for production of fabric that is ultimately cut and sewn into apparel, and therefore, the gap in yarn supply is supplemented by imports.
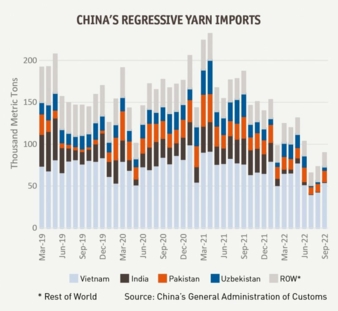
Yarn imports have plunged
From January to September 2022, China imports of cotton yarn fell by nearly half from the same period last year. This decline is equivalent to roughly 760,000 tonnes of cotton lint and is the lowest level in more than a decade. Lower yarn imports and domestic cotton consumption are driven in part by domestic Covid lockdowns, foreign trade policies barring imports of China’s cotton products, and slowing global demand for apparel.
Slower domestic and foreign demand for China’s apparel is exhibited by slowing domestic apparel sales and cotton product exports, which each fell five percent in January - September 2022 compared with the previous year. The decline in China yarn imports has helped to lower cotton consumption in major yarn exporting countries which include India, Vietnam, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan. China was the largest foreign market for each major yarn exporter last calendar year.
Imports less competitive
Chinese yarn prices are relatively lower than similar quality grades for imported yarn, a departure from recent history. China’s lower domestic cotton lint prices and Covid lockdowns have pressured domestic yarn prices and made imports less competitive.
China yarn imports have recently been a recent bellwether for global cotton consumption growth prospects, and plummeting cotton yarn import demand is helping to pressure 2022/23 global cotton use. World cotton lint consumption is projected at 25.02 million tonnes, down 520,000 tonnes from last year and 1.79 million tonnes below the level witnessed two years ago.
Source: USDA, World Markets + Trade, 11/2022
Bremen Cotton Exchange – Issue 45-46/2022, Bremen Cotton Report