03.01.23 – Economy
Major concern about the EU textile industries’ competitiveness
The EU textiles industry is highly concerned about the potential loss of competitiveness, caused by the EU’s inaction of the energy crisis, and Chinese and US subsidies to domestic industry.
Following the European Council summit and its conclusions on the measures to tackle the energy crisis, the European textiles industry is extremely concerned about the fast loss of competitiveness of Europe and demands urgent action to save the industry.
There is no business case to invest in Europe
The chain of factors determining this sharp decline in the competitiveness is twofold. First, the energy cost in Europe is more than 6 times higher than in the US, China, and neighbouring countries. This factor alone has almost erased the business case for producing in the EU. At present, many textiles and clothing companies are producing at net loss or have shut down production. The industrial conditions have worsened in such a way that there is no business case to invest in Europe or buy products produced or processed in the EU. It is only the sense of responsibility of the entrepreneurs towards the European society that is keeping the plants and production running.
Secondly, while the EU is passive and extremely slow in articulating a credible and effective response to the energy crisis, our main international competitors and trade partners (China, India and the US respectively) have developed comprehensive state-aid frameworks for their domestic industry despite not being affected by this crisis at all. The latest example is the 369-billion-dollar scheme of the Inflation Reduction Act rolled out by the Biden administration.
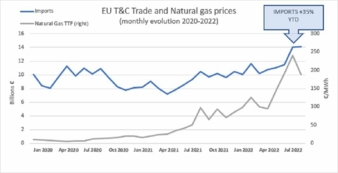
Recent trade data already indicate a loss of global competitiveness: imports to the EU have grown tremendously in 2022 (+35% year-to-date). It is also evident that the surge in imports goes in parallel with the surge of natural gas price. It is expected that energy prices will remain high and volatile, opening the door for imports to gain substantial market shares in the EU.
An ambitious and comprehensive relaunch plan is needed
The market situation has eased somewhat since in the past months, but the crisis remains because gas prices are still extremely high in comparison to last year. This suggests that the current loss of competitiveness of the EU manufacturing will not be recovered even with lower energy prices, unless measures are taken to correct the unlevel playing field on which the EU industry has to operate in the international markets. Only with an ambitious and comprehensive relaunch plan at EU level, Europe will be able to restore its credibility as a global manufacturing powerhouse and investments .
If the status quo is maintained, not only the EU will not be able to recover its competitive position on the global business stage, but it will also fail its plans to reach zero-net emissions and achieve circularity. It is evident that these ambitions need massive capital investments. However, in the current scenario we can only expect an investments diversion to markets where governments are actively supporting those investments and energy costs are much lower – regardless of their fossil- or non-fossil origin.
Actions necessary to ensure survival of SMEs
The whole value chain, from fibres, nonwoven, to fabrics, clothing manufacturers, is facing unprecedented pressure deriving from the current geopolitical situation, the new macroeconomic conditions and unfair competition from third states. The situation is going to worsen if no emergency action is taken, especially because a recession is expected in the coming months.
The main structural component of the EU manufacturing are SMEs: these are economic actors that are particularly exposed to the current crisis as they do not have the financial leverage to absorb the impact of energy prices for much longer. Urgent EU action is needed to ensure their survival.